
The Internet is a wonderful thing. It has led to the creation of so many innovations and ways of life that it’s hard to point out just one. But, as with everything else in this world, there are some downsides.
In this blog post, we will discuss the ipv4 vs ipv6 rivalry.
One major concern for the future is whether or not we will have enough IP addresses for all these devices that connect online each day.
As time goes on and more people buy laptops, smartphones, tablets, TVs – you name it – the fear of running out of IPv4 addresses becomes more real every day.
We’re already seeing companies like Google roll out their products without any IPv4 address at all!
We can also determine how IPv6 has done a major job in the evolution of the internet, and how it is more advanced than its successor IPv4.




What is IPv4?
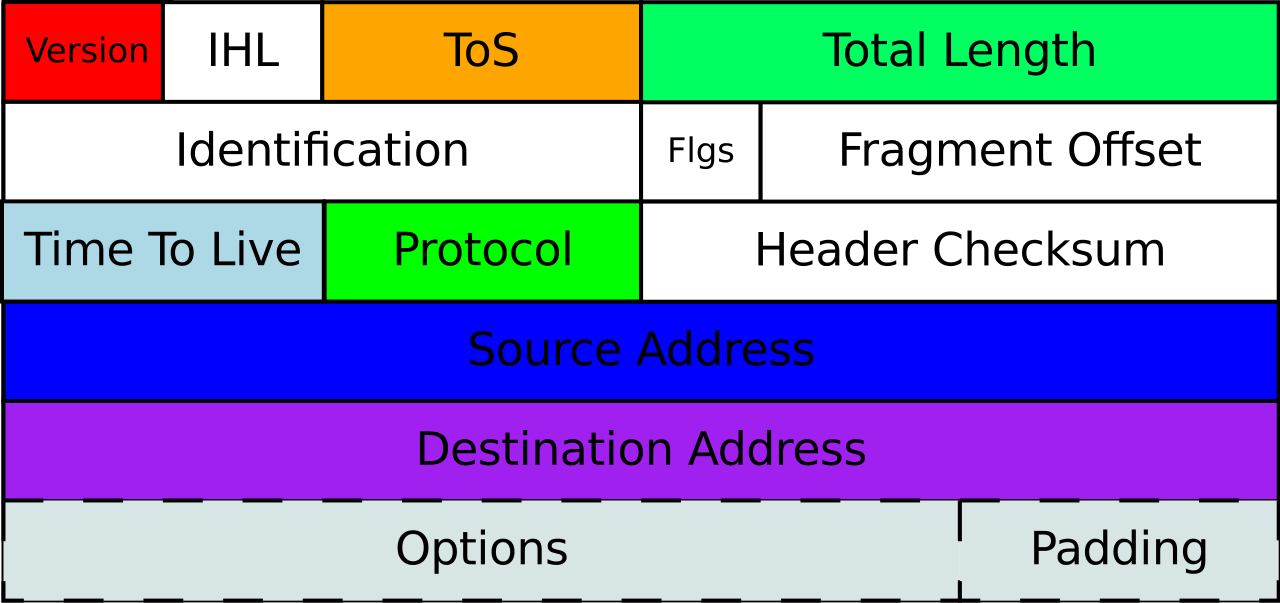
IPv4 is the protocol that a lot of devices on the Internet use for device identification. It may be static or dynamic. The first generation version of IP, IPv4, was deployed in 1983. It uses a 32-bit address scheme which gives it more than 4 billion addresses. IPv4 is the primary Internet protocol and carries 94% of internet traffic.
IPv4 Features?
Below are the features of IPv4:
Also provides Connectionless Protocol.
Allow generating a simplistic virtual communication layer above diversified devices.
It needs more limited memory and the comfort of remembering and reading addresses.
Already supported by millions of devices worldwide.
conferences and video libraries are also offered.
IPv4 future
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to rapidly grow, more and more devices are connecting online every day. This unprecedented growth rate is starting to make addresses unavailable, which means we need IPv6 deployment for long-term global internet growth.
The use of internet-connected devices is going up exponentially, and there’s a finite supply of IP addresses. In the month of October 2019, RIPE NCC announced it had one million (1M) IPv4 addresses left.
Just because of this limited number of available IP addresses, IPv6 (Internet protocol 6) has been launched as a standardized and stable solution. Using 128-bit address lengths, it can define up to 2128 devices.
Device addresses are becoming exhausted, and shortages may start occurring within the next few years.
The concern is rising that solutions for the Internet of Things (specifically, limited IP addresses) are soon going to be very complicated and not very cheap.
As addresses near depletion, there is a need for enterprises worldwide to hold the stock of IP resources and find solid solutions in preparation for IPv6 distribution and deployment.
Until IPv4 addresses are no longer an issue, it is possible to lengthen the lifetime of these aging IPs by implementing (CGNAT). To avoid running out of IP addresses, CGNAT assigns one IP address to many devices. When more is needed, it cannot scale infinitely.
With the addition of every additional device, NAT becomes more complex and more likely to fail. Even worse, when a failure occurs, an effect on thousands of devices is felt and can not be fixed quickly.
One way to extend the life of IPv4 addresses is by selling unused or which are not needed, this gap in supply and demand means you can make a profit. But it’s also risky because prices are dictated by supply and demand, so you have upkeep costs run on top of your original outlay.
IPv4 lassitude stretches back to 2012 when the (IANA) Internet Assigned Numbers Authority assigned the last IPv4 addresses to (RIPE NCC).
What is IPv6?
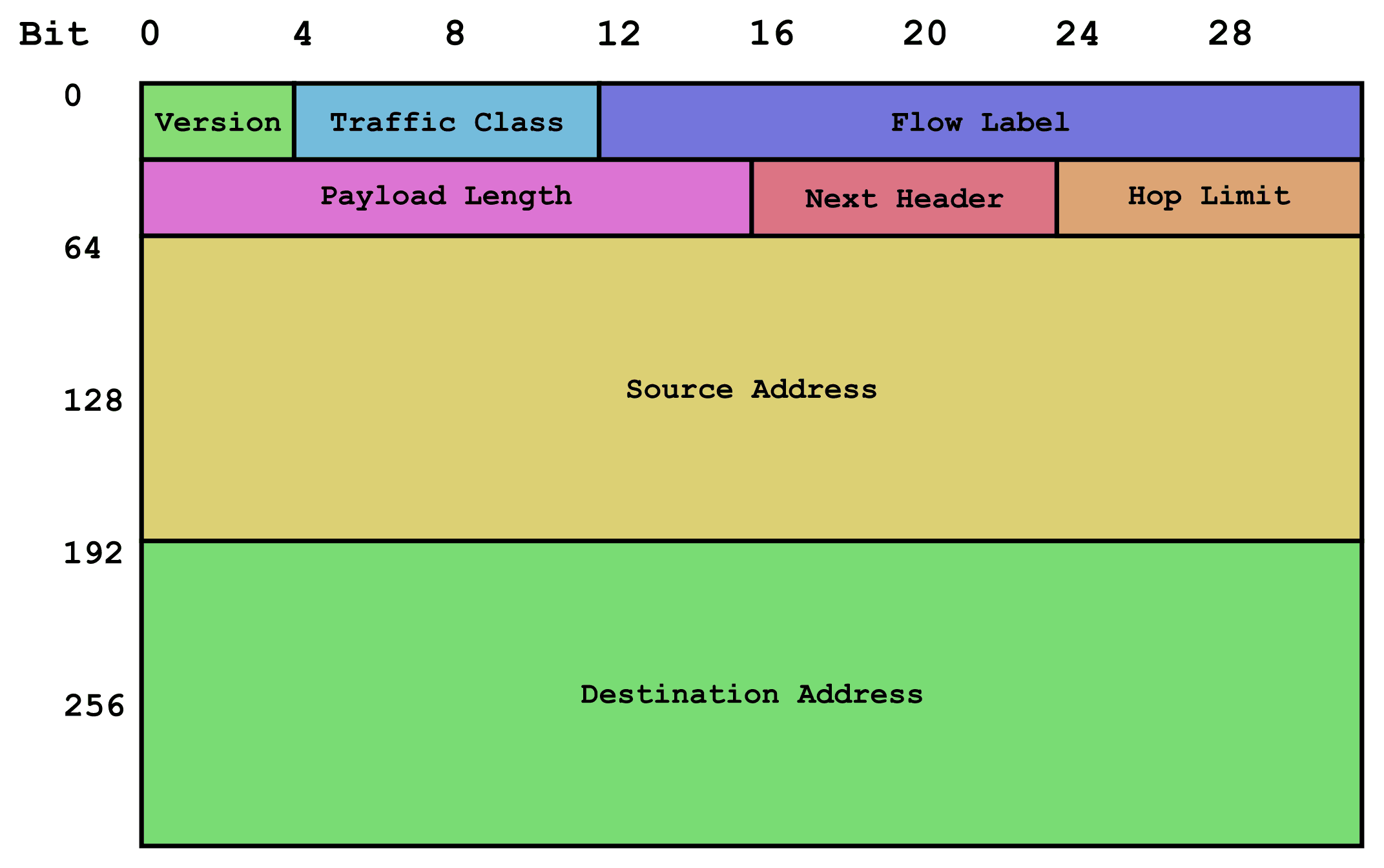
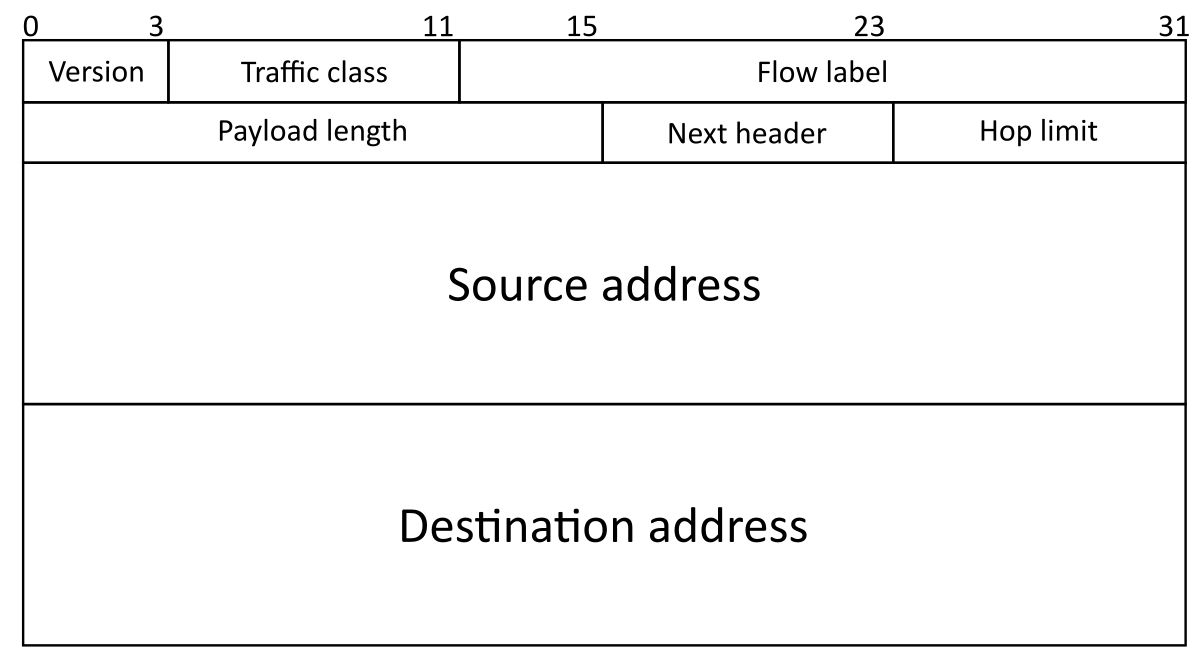
IIPv6 is the newest iteration of the IP address. The newer version of the Internet protocol is proposed as an enhancement of the older Internet Protocol version 4 (IPV4), which supports a greater number of devices than the older version.
Since addresses will run out one day, IPv6 is an upcoming system that allows for up to 2128 possible address combinations. The IPv6 address format was made in the (hexadecimal) form.
This allowed for more expansion, with eight octets as opposed to four. September 20, 1984, was the date the first address book became available, and it has seen many releases since.
IPv6 Features?
Below are the features of IPv6:
Hierarchical addressing system and routing foundation
Stateful and Stateless arrangement
Support for quality of service (QoS)
An excellent protocol for adjacent node communication.
Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6 Addresses
| IPV4 | IPV6 |
| IPv4 is a 32-Bit IP Address. | IPv6 is a 128 Bit IP Address. |
| Mac addresses are being mapped by Resolution Protocol. |
To map MAc addresses NDP protocol is used (neighbor discovery). |
| Has checksum fields |
Does not have checksum fields |
| Unicast, broadcast, and multicast. |
Unicast, multicast, and anycast. |
| For Broadcasting ARP. |
For Multicast Neighbor Solicitation. |
Pros and Cons of using IPv6
Below are the advantages and disadvantages of IPv6.
- Efficient Routing
- Multi Routing
- Directed Local Address
- Directed Local Address
- Complexity in the Network Topology Drawings
- Upgrading the devices
- Local Networking Changes
- Confusion in the IP Schemes
What is an IP address?
Internet Protocol (IP) is the numerical label assigned to each device connected to a network that uses this protocol. An IP address is an identifier for a device on a network.
How does an IP address work?
Information or traffic-utilizing distinctive addresses. Every smartphone(Android & iOS) or computer connected to the Internet is assigned an IP address.
To connect to the internet, each device needs an IP address.
IP+TCP identifies connections on a network and authorizes virtual connections between ( point A to B) source and destination.
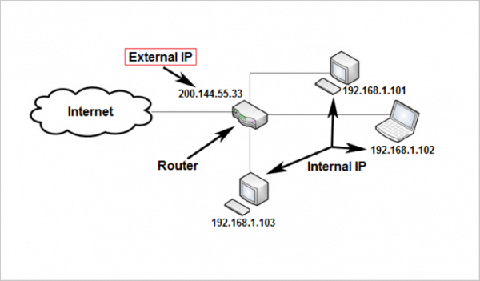
IP+TCP is identifying the devices that are connecting to a network. And what it’s doing for IoT is enabling communication between sources (such as smart fridges) and destinations (like apps). Without a unique IP address, your device would not be able to interact with the network.
Frequently asked questions
Which is faster IPv4 or IPv6?
What is IPv6 used for?
Does IPv6 completely replace IPv4?
Should I use IPV4 or IPV6?
What's better for gaming IPV4 or IPV6?
Can I use IPV4 and IPV6 at the same time?
Do I need to change IPV4 and IPV6 DNS?
Does IPV6 increase internet speed?
What advantages does IPv6 have over IPv4?
Does IPv4 and IPv6 affect Internet speed?
Will IPv4 coexist with IPv6?
Conclusion
Websites will need to use a gateway system that supports IPv4 just to communicate with the devices still using the older protocol. Adding the IPv6 standard addresses to IPv4 will help with an increasing shortage of IP (Internet Protocol) addresses. Thanks for reading this article on IPv4 Vs IPv6.